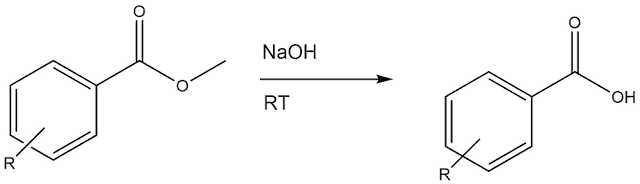
 |
| Example of a hydrolysis reaction from carboxylate to carboxylic acid, drawn by myself. |
The reaction shown is an example of a common hydrolysis reaction used in organic chemistry.
The ester compound on the left (carboxylate moiety), is usually dissolved in 1,4-dioxane. Then, NaOH aqueous solution is added.
Conditions are dependent of the type of compound.
Several conditions can be used:
- 80 °C, 2 M NaOH, if compound is extremely stable, these are harsh conditions.
- 80 °C, 1 M NaOH
- 60 °C, 2 M NaOH
- Room temperature (RT), 2 M NaOH
- RT, 1 M NaOH
If the compound is susceptible to degradation or is unstable, use room temperature and a low molarity of NaOH. It all depends on the compound of course, and often knowledge is obtained by trial and error. It is advised to start with the least harsh conditions.
When hydrolysis is complete, isolation of the final compound is done by evaporating the solvent (1,4-dioxane), acidify with HCl or an ion exchange resin, and filter off the precipitation. Dry the obtained solid and analyse.
Comments
Post a Comment